Top Transfer Switch Types for Reliable Power Management?
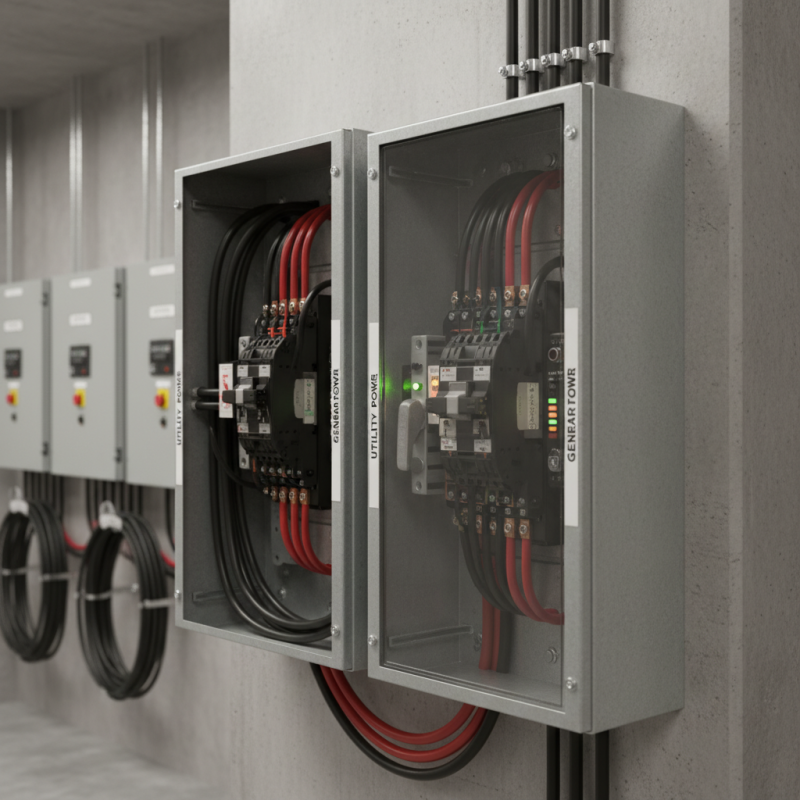
In today's world, reliable power management is essential. A crucial component in this system is the Transfer Switch. This device manages the transition between different power sources, ensuring continuous electricity supply. A good Transfer Switch ensures that outages are handled seamlessly.
Understanding the types of Transfer Switches available can be overwhelming. Different models serve various needs. Some are automatic, switching without user input. Others require manual operation. Each type has its strengths and weaknesses. Selecting the right one may reflect your specific requirements.
Consider the reliability of your power sources. Frequent outages can lead to critical issues. Investing in the appropriate Transfer Switch can mitigate risks. Reflect on your power management strategy and ensure it includes a robust Transfer Switch. The choice can affect both safety and convenience in your daily life.
Types of Transfer Switches and Their Applications
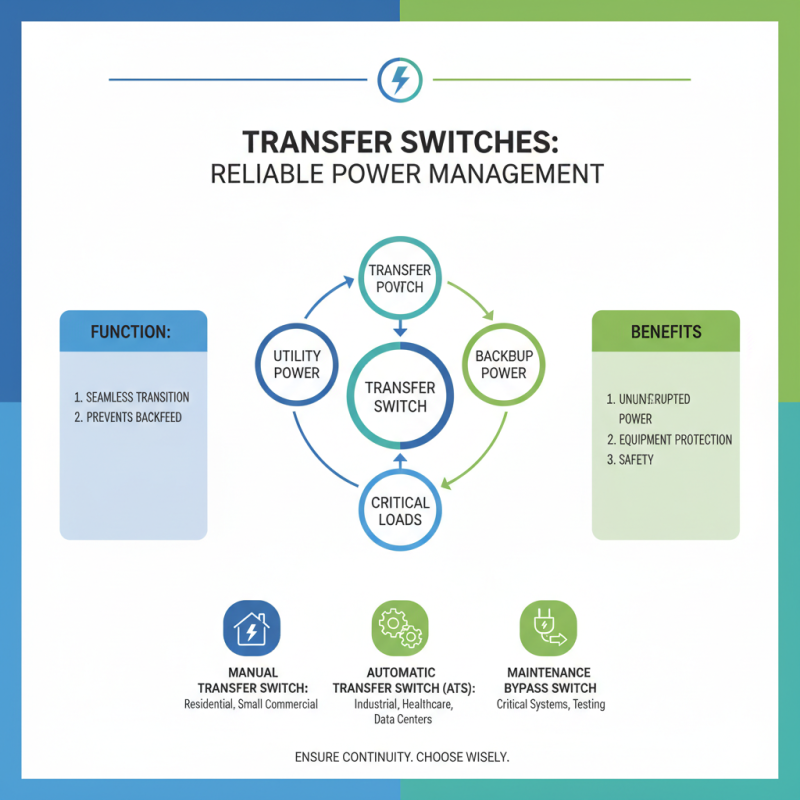
Transfer switches are essential for reliable power management. They ensure a seamless transition between utility and backup power sources. Various types cater to different applications.
Manual transfer switches require user intervention. Users must physically switch from one power source to another. This setup suits small homes or businesses where power interruption is manageable. However, relying on manual operation can lead to delays during emergencies.
Automatic transfer switches (ATS) offer a higher level of convenience. They detect power outages and switch automatically within seconds. ATS is ideal for critical infrastructure, such as hospitals or data centers. Yet, these systems can fail if not regularly maintained, leading to unplanned downtime.
**Tips**: Regular maintenance of both types is vital. Test all components frequently. Additionally, ensure clear access to switches, especially manual ones. This step saves crucial time during outages.
In conclusion, various transfer switches serve distinct roles. Choosing the right type depends on your specific needs and situations. Overlooking any option can lead to unexpected complications. Consider power requirements and potential outages carefully.
Understanding Manual vs. Automatic Transfer Switches
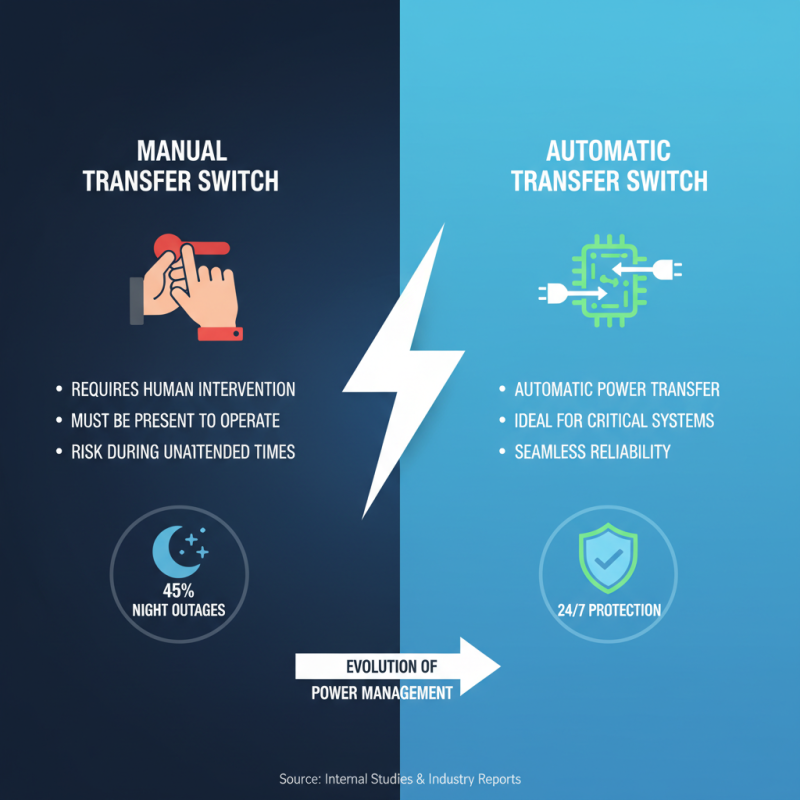
Manual and automatic transfer switches (ATS) play crucial roles in power management. Manual transfer switches require human intervention to switch power sources. Users must be present to operate them. For critical applications, this can be a drawback. In fact, studies show that 45% of power outages occur during the night when personnel might not be available.
Conversely, automatic transfer switches monitor power supply continuously. They can detect outages and switch sources seamlessly. Industry reports indicate that over 70% of businesses employing ATS experience fewer operational disruptions. This can lead to significant cost savings and increased reliability. However, automatic systems can be complex. Failure rates can rise due to maintenance oversight, leading to risks during outages.
Choosing between manual and automatic switches depends on specific needs. Businesses must evaluate their risk tolerance and operational requirements. Some settings may benefit from the simplicity of manual switches. Others might prioritize the efficiency of automatic systems. Both options have their advantages and pitfalls. Reliable power management entails careful consideration of these factors.
Key Features of Essential Transfer Switch Types
Transfer switches are critical for seamless power management. They ensure an uninterrupted power supply during outages. There are several types widely used, each tailored to specific needs.
Manual transfer switches provide a cost-effective solution for many homes. They require users to switch the power source manually. This can lead to occasional oversights when transferring power. Automatic transfer switches, on the other hand, sense outages and switch automatically. Reports indicate that these switches enhance reliability. Over 75% of businesses rely on automatic systems to mitigate downtimes.
Key features of transfer switches include load capacity and safety measures. A switch's load capacity must match the connected power source. Safety features, such as lockout systems, prevent accidental activation. The National Electrical Code stresses the importance of proper installation. Yet, improper setups are often reported, leading to dangerous situations. Detailed planning and assessment are essential to avoid pitfalls.
Top Transfer Switch Types for Reliable Power Management
This chart illustrates the ratings of different types of transfer switches based on their essential features for reliable power management. The Automatic Transfer Switch offers the highest reliability, followed by Static Transfer Switch, Bypass Isolation Switch, and Manual Transfer Switch.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Transfer Switch
When selecting a transfer switch, several factors play a crucial role. One main aspect is the switch’s capacity. It must handle your power needs during outages. A switch with too little capacity could lead to overload. This may cause unexpected failures or, worse, damage to connected devices.
Location is another critical consideration. Where will you install the transfer switch? It should be easily accessible for maintenance or emergencies. A poorly placed switch may complicate the situation during a blackout. Additionally, think about your budget. While advanced features are appealing, excessive spending might not be wise. Balancing cost with functionality is vital.
Compatibility with generators is equally important. Ensure the transfer switch works seamlessly with your generator model. Some users overlook this aspect and face connection issues. Lastly, consider the type of transfer switch: manual or automatic. Automatic switches are convenient but can be more expensive. Reflecting on these factors will help you make a better decision.
Best Practices for Maintenance and Operation of Transfer Switches
Effective maintenance and operation of transfer switches are crucial for ensuring reliable power during outages. According to a report by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, nearly 70% of power failures are caused by equipment issues. Regular inspection can significantly reduce this risk. Inspecting connections, testing load capacities, and checking the controls should be routine tasks for operators.
Documentation is often overlooked. Keeping accurate records of maintenance activities provides insight into performance trends. This process identifies potential issues before they escalate. Data from the National Fire Protection Association shows that well-maintained systems can lower operational risks by up to 40%. Regular monitoring of the transfer switch’s functionality minimizes downtime and enhances system reliability.
Additionally, training personnel is vital. Operators should be educated about best practices and emergency procedures. Missteps can lead to costly errors. In fact, a survey found that untrained personnel are linked to over 50% of transfer switch failures. Investing in training may seem trivial, but it pays off in the long run. Power management is not just about the equipment; it is also about the people managing it.

Home
About Us
Products
News
Blog
Contact Us
 Sinotruk Parts
Sinotruk Parts
 Shacman Parts
Shacman Parts
 FAW Parts
FAW Parts
 Dongfeng Parts
Dongfeng Parts
 Foton Parts
Foton Parts
 CHENGLONG PARTS
CHENGLONG PARTS
 Golden Dragon Bus Parts
Golden Dragon Bus Parts
 King Long Parts
King Long Parts
 Yutong Parts
Yutong Parts
 Higer Parts
Higer Parts
 Zhongtong Parts
Zhongtong Parts
 Ankai Parts
Ankai Parts



 Mr. Perry Wu International Sales Director
Mr. Perry Wu International Sales Director